Want to learn how to run genboostermark python in online without installing anything on your computer? You’re in the right place. Many people search for “genboostermark,” but the correct library name is genbooster a fast Python package used for gradient boosting and machine learning tasks like classification and regression.
Running genbooster online is like borrowing a powerful computer in the cloud. You don’t need to set up Python, configure Rust, or worry about system errors. Platforms like Google Colab let you write code, install packages with pip, and train models in minutes — all inside your browser.
This guide will show you exactly how to run genboostermark python in online step by step. Whether you’re a beginner learning machine learning or a student testing a quick model, you’ll be able to install genbooster, train a classifier, and see real results fast and hassle-free.
What Is Genboostermark (Genbooster) in Python?
If you’ve been searching for genboostermark, you’re not alone. Many users type this term when looking for a machine learning library. However, genboostermark is not an official Python package. The correct name is genbooster, a powerful tool designed for fast gradient boosting and bagging in Python.
Is Genboostermark a Real Package?
No, “genboostermark” does not exist on PyPI or GitHub. It’s simply a common misspelling of genbooster. The actual library is available on PyPI for easy installation using pip, and its source code is hosted on GitHub for developers who want deeper access.
Genbooster stands out because it combines Rust and Python. Rust handles performance-heavy operations, while Python keeps the interface simple and user-friendly. This hybrid approach makes gradient boosting faster and more efficient compared to many traditional implementations.
If you’re new to boosting algorithms, you may want to read our guide on What Is Gradient Boosting in Python? to better understand how the technique works.
Key Features of Genbooster
Genbooster includes several features that make it ideal for machine learning projects:
- Fast gradient boosting for improved model performance
- Bagging techniques to reduce overfitting
- Support for classification and regression tasks
- Designed to work smoothly with scikit-learn tools and workflows
In simple terms, genbooster helps you train smarter models faster — without complex setup or heavy configuration.
Best Platforms to Run Genboostermark Python in Online
Choosing the right platform makes all the difference. Since genboostermark actually refers to genbooster, you’ll need an online Python environment that supports pip installation and machine learning libraries. The good news? Several cloud-based coding platforms let you run Python code directly from your browser — no local setup required.
Let’s look at the best options.
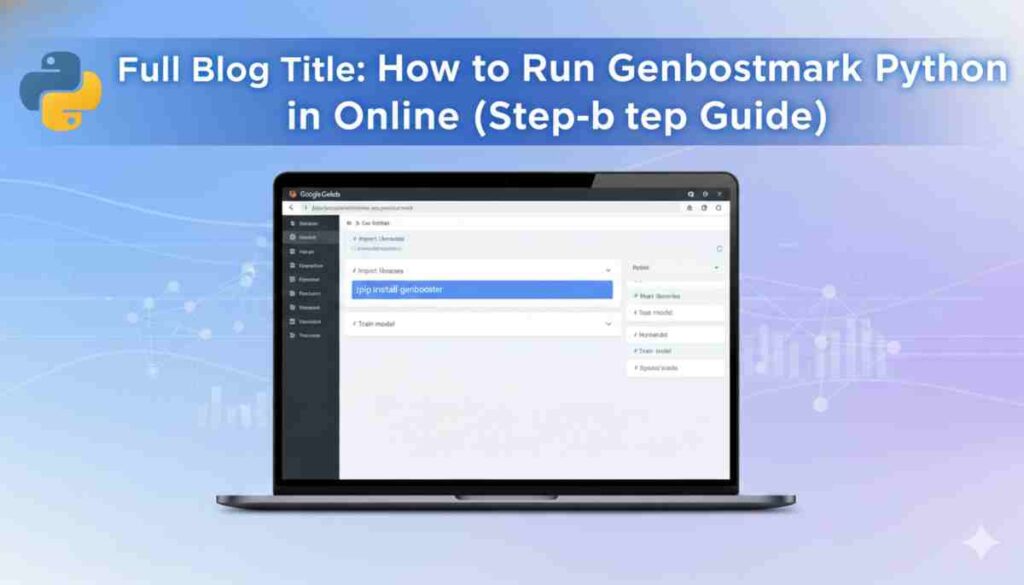
1. Google Colab (Recommended)
Google Colab is the most popular choice for running Python machine learning projects online. It works like a cloud-based Jupyter notebook, meaning you can write code in small cells and execute them step by step.
Here’s why it stands out:
- ✅ Free access to GPU and TPU
- ✅ No installation or configuration needed
- ✅ Full Jupyter notebook support
- ✅ Easy
pip installfor packages like genbooster
You simply open a new notebook, run !pip install genbooster, and start building your model. It’s ideal for students, beginners, and even professionals testing ML algorithms.
2. Replit
Replit is another browser-based coding platform that supports Python execution. It allows you to create projects, install packages, and run scripts online.
Key benefits:
- 💻 Fully browser-based coding
- 👥 Real-time collaboration features
- 📦 Supports
pipinstallations
Replit is great for collaborative projects or quick testing. However, it may not be as powerful as Colab for heavy machine learning workloads.
3. JDoodle
JDoodle is best for running quick Python scripts without creating an account.
Advantages:
- ⚡ Fast script execution
- 🌐 Runs directly in the browser
Limitations:
- ❌ Limited support for large ML libraries
- ❌ Not ideal for training complex models
Platform Comparison
| Platform | Free | Supports pip | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Google Colab | Yes | Yes | Machine learning & GPU tasks |
| Replit | Yes | Yes | Collaboration & small projects |
| JDoodle | Yes | Limited | Quick script testing |
For most users learning this, Google Colab remains the best and most reliable option.
Step-by-Step: How to Run Genboostermark Python in Online Using Google Colab
If you’re serious about learning how to run genboostermark python in online, Google Colab is the easiest and most reliable method. Since genboostermark refers to genbooster, you only need a browser and a Google account to get started. No local Python setup. No Rust installation. Everything runs in the cloud.
Follow these simple steps.
Step 1: Create a Google Colab Notebook
First, go to Google Colab and sign in with your Google account.
Click “New Notebook.” A fresh Jupyter notebook will open in your browser. Think of it as an online coding workspace where you can write and run Python code in separate cells.
Google Colab already has Python installed, so you don’t need to configure anything. That’s the beauty of cloud-based machine learning environments — they remove technical barriers so you can focus on building models.
Step 2: Install Genbooster
Now you need to install the genbooster library directly from PyPI.
In the first code cell, type:
!pip install genbooster
Press Shift + Enter to run the cell.
The ! symbol tells Colab to run a system command. The pip install command downloads and installs the genbooster package from the official PyPI repository.
Once completed, you’ll see a success message confirming the installation.
Step 3: Verify Installation
After installation, it’s important to confirm everything works correctly.
In a new cell, type:
import genbooster.genboosterclassifier
Run the cell.
If no error appears, congratulations — genbooster is installed successfully. If you see a ModuleNotFoundError, restart the runtime and try again.
This verification step ensures your Python environment recognizes the machine learning library before you begin training models.
Step 4: Alternative GitHub Installation
If you want the latest development version instead of the PyPI release, you can install directly from the official GitHub repository.
Run this command:
!pip install git+https://github.com/Techtonique/genbooster.git
This method pulls the newest version of the code straight from GitHub.
That’s it. You’ve successfully learned how to run genboostermark python in online using Google Colab. In just a few minutes, you created a cloud notebook, installed a gradient boosting library, and verified your setup — all without touching your local machine.
Basic Genbooster Classifier Example (With Iris Dataset)
Now that you’ve learned how to set up the environment, let’s build a simple machine learning model using Genbooster. This example uses the famous Iris dataset to demonstrate how the BoosterClassifier works in a real-world scenario.
Think of this process like teaching a student. You show the model examples (training data), test what it learned (predictions), and then measure how well it performs (accuracy).
Import Required Libraries
First, import the necessary Python libraries:
import numpy as np
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import ExtraTreeRegressor
from genbooster.genboosterclassifier import BoosterClassifier
Here’s what each part does:
load_irisloads a built-in dataset.train_test_splitdivides data into training and testing sets.ExtraTreeRegressoracts as the base learner.BoosterClassifierbuilds a boosted ensemble model.
The BoosterClassifier combines multiple weak models into a stronger predictive model using gradient boosting techniques.
Load Dataset & Split Data
Next, load and split the dataset:
X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(
X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42
)
Here, 80% of the data is used for training, and 20% is reserved for testing. This helps evaluate how well the model performs on unseen data.
Train BoosterClassifier
Now, initialize and train the model:
clf = BoosterClassifier(base_estimator=ExtraTreeRegressor())
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
The fit() method trains the model using the training dataset. Behind the scenes, boosting reduces prediction errors step by step, improving performance with each iteration.
Evaluate Accuracy
Finally, test the model:
preds = clf.predict(X_test)
print(np.mean(preds == y_test))
Accuracy is calculated by comparing predicted values (preds) with actual labels (y_test). The formula is:
Accuracy = Correct Predictions ÷ Total Predictions
If the output is 0.95, it means 95% of predictions were correct.
How to Adapt This for CSV Data
If you have your own dataset in a CSV file, use pandas:
import pandas as pd
data = pd.read_csv("your_file.csv")
X = data.drop("target_column", axis=1)
y = data["target_column"]
Then follow the same training steps.
With this example, you now understand how Genbooster trains, predicts, and evaluates a classification model using real data.
Common Errors and How to Fix Them
Small errors in Python can feel frustrating. The good news? Most problems are simple to fix. Since genboostermark refers to genbooster, issues usually relate to installation, environment setup, or runtime behavior in platforms like Google Colab.
Let’s go through the most common errors and their solutions.
ModuleNotFoundError
This error usually appears as:
ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'genbooster'
It means the package is not installed in your current runtime session.
How to fix it:
- Run
!pip install genboosteragain. - Make sure you executed the installation cell successfully.
- Restart the runtime and re-run all cells if needed.
Online platforms reset environments sometimes, so you may need to reinstall packages each session.
Version Conflicts
Sometimes, genbooster may conflict with existing Python or scikit-learn versions. This can cause import errors or unexpected behavior.
How to fix it:
- Upgrade pip:
!pip install --upgrade pip - Update dependencies:
!pip install --upgrade scikit-learn - Use a fresh Google Colab notebook to avoid package clashes.
Keeping libraries updated ensures compatibility with machine learning tools.
Runtime Restart Issues
After installing packages, Google Colab may require a runtime restart. If you try importing immediately, it might fail.
How to fix it:
- Click Runtime → Restart runtime
- Re-run all cells from top to bottom.
Think of it like rebooting your computer so changes can take effect.
Quick Troubleshooting Table
| Error Type | Cause | Solution |
|---|---|---|
| ModuleNotFoundError | Package not installed | Run pip install genbooster |
| Version Conflicts | Library mismatch | Upgrade pip & dependencies |
| Import still failing | Runtime not refreshed | Restart runtime and rerun |
Most issues when running genboostermark python online are temporary and easy to solve with these quick fixes.
Why Run Genbooster Online Instead of Locally?
You might wonder why not just install everything on your computer. The answer is simple: running genbooster online is easier, faster, and more beginner-friendly.
First, there’s no local installation required. You don’t need to install Python, configure environments, or manage dependencies. Platforms like Google Colab already come with Python and essential data science libraries pre-installed. You just open a notebook and start coding.
Second, there’s no Rust setup required. Since genbooster combines Rust and Python for performance, setting it up locally can sometimes feel technical. Running it online removes that complexity. The cloud environment handles everything behind the scenes.
This approach is especially helpful for students and beginners. If you’re learning machine learning or testing gradient boosting models, you can focus on understanding the algorithm instead of troubleshooting system errors.
Finally, online platforms allow faster experimentation. You can test ideas, train models, and share notebooks instantly. It’s like having a ready-to-use machine learning lab — available anytime, from any device.
Conclusion
Now you clearly understand how to run genboostermark python in online using a simple and practical approach. Even though “genboostermark” is a common misspelling of genbooster, the process is straightforward once you know the right steps. By using Google Colab, you avoid local installation, skip complex setup, and start building machine learning models in minutes.
From installing the package with pip to training a BoosterClassifier and fixing common errors, everything can be done directly in your browser. It’s fast, beginner-friendly, and perfect for experimenting with gradient boosting algorithms.
If you haven’t tried it yet, open Google Colab and test it yourself. Within a few clicks, you’ll see how easy it is to run genbooster online and bring your Python machine learning projects to life.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Below are quick, clear answers to common questions about using genbooster for machine learning.
Can I run genboostermark without installing Python?
Yes, you can run genboostermark (genbooster) without installing Python on your computer. Platforms like Google Colab already have Python pre-installed in the cloud. You simply open a notebook, run !pip install genbooster, and start coding.
This means you don’t need to download Python, configure environments, or manage local dependencies. Everything runs inside your browser, making it ideal for beginners and students.
Is Google Colab free for machine learning?
Yes, Google Colab offers a free tier that supports most machine learning tasks. You get access to cloud-based CPUs, and in many cases, free GPUs and TPUs.
For basic gradient boosting, classification, and regression tasks using genbooster, the free version is usually more than enough. However, heavy or long-running training jobs may have session limits.
Does genbooster support regression tasks?
Yes, genbooster supports both classification and regression problems. While many examples focus on classification (like the Iris dataset), you can train regression models by providing numerical target values.
The boosting technique works by reducing prediction errors step by step, whether you’re predicting categories or continuous values.
Is genboostermark different from genbooster?
No, genboostermark is not a separate package. It is simply a common misspelling of genbooster. The official library is available on PyPI and GitHub under the name genbooster.
Read Also: GRS Uine28.6 Error Codes: Meaning, Causes, and Easy Fixes